Oriental photinia can protect against skin aging: Study
10/05/2020 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
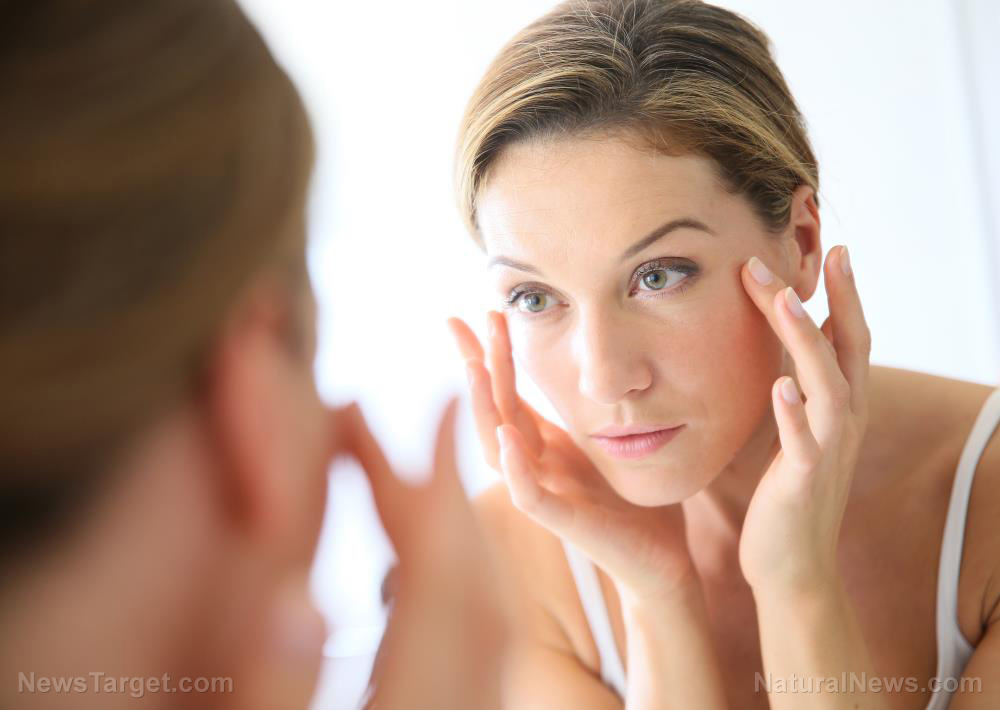

Pourthiaea villosa, commonly known as oriental photinia or Christmas berry, is a flowering shrub that belongs to the rose (Rosaceae) family. It is native to East Asia, particularly to Japan, Korea and China. Oriental photinia has edible leaves and fruits, as well a hard and heavy wood that’s suitable for making furniture. Although not much is known about its medicinal uses, oriental photinia appears to be a rich source of anti-inflammatory compounds, according to one study.
In a more recent endeavor, researchers from South Korea and the U.S. decided to investigate whether oriental photinia has antioxidant and anti-aging properties. They tested an extract obtained from oriental photinia on cultured human skin cells and found that it contains several active components that can scavenge free radicals and increase the production of antioxidant enzymes.
The researchers reported their findings in an article published in the Journal of Medicinal Food.
Oriental photinia can protect the skin from free radicals and oxidative damage
Skin aging has been linked by numerous studies to an increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by cells. Because these harmful free radicals are the main contributors to premature aging, skin cells developed their own way of protecting themselves from ROS-induced damage in the form of antioxidant enzymes. These antioxidants play a critical role in preventing ROS-induced aging.
To test the antioxidant and anti-aging activities of oriental photinia, the researchers treated human dermal fibroblast (HDF) cells with an extract derived from the plant. Part of their objective was to determine the mechanisms underlying the extract’s effects.
The researchers reported that oriental photinia extract showed significant antioxidant effects based on evaluations of its reducing power and free radical scavenging activity. The extract also significantly increased the expression of antioxidant enzymes in HDFs.
In addition, the oriental photinia extract effectively blocked hydrogen peroxide-induced matrix metalloproteinase activity by influencing the MAPK signaling pathways. According to studies, matrix metalloproteinases are enzymes involved in premature aging.
The oriental photinia extract was found to contain active compounds like polyols, phenolic compounds and flavonoids.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that oriental photinia has potent antioxidant and anti-aging effects that can fight premature aging. (Related: Achieve younger looking skin with these anti-aging foods.)
Other medicinal plants with anti-aging properties
Skin aging can be accelerated by various factors, such as genetic mutations, excessive exposure to the sun and environmental pollutants, poor diet and an underlying disease. Fortunately, many medicinal plants contain active components that can delay skin aging. Here are some of the best medicinal plants you can use to keep your skin looking young and healthy. (h/t to EssentialHomeAndGarden.com)
- Calendula — A soothing medicinal herb that reduces inflammation, treats acne and promotes faster skin healing.
- Aloe vera — A natural moisturizer that can soothe inflamed skin.
- Echinacea — This herb can help treat acne, reduce inflammation and promote skin regeneration.
- Green tea — Well-known as healthy drink, green tea also has antioxidant properties that can improve aging skin.
- Lavender — Lavender oil has antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties and can also speed up skin healing.
- Thyme — A popular culinary herb, thyme contains benzoyl peroxide that can help clear out acne.
- Rose — Rose water is not only gentle to the skin, it can also help reduce inflammation and boost regeneration while moisturizing the skin.
- Rosemary — Another culinary herb with skin-boosting properties, rosemary can stimulate blood flow to the skin and promote healing.
- Cucumber — Often used to moisturize and soothe the skin, this common fruit can also reduce puffiness, tighten the skin and relieve skin irritation.
Skin aging may be inevitable, but it can be delayed with proper skin care and nourishment. Adopting a healthy diet, for instance, can help supply your skin with all the essential nutrients it needs to stay youthful-looking and maintain a healthy glow. You can also use medicinal plants like aloe vera, cucumber and green tea on your skin to fight the signs of skin aging naturally.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
aging secrets, alternative medicine, anti-aging, antioxidants, Free radicals, herbal medicine, Herbs, natural cures, natural medicine, oriental photinia, phytonutrients, plant medicine, prevention, research, skin aging, skin health
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 PHYTONUTRIENTS NEWS