Cyanidin sources, health benefits and uses
09/18/2017 / By Earl Garcia

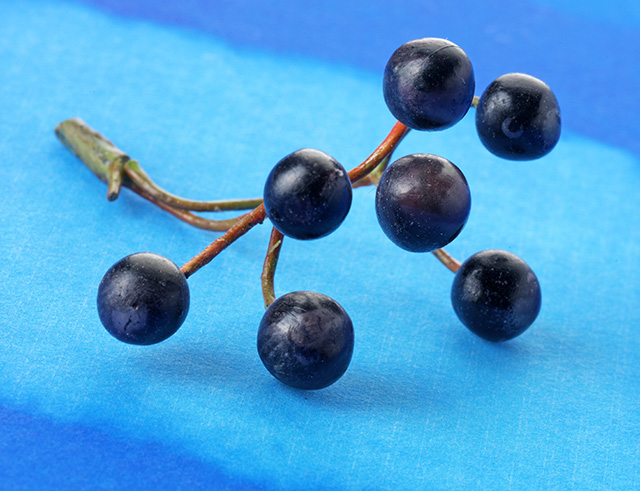
Cyanidin is a water-soluble pigment that belongs to a group of anthocyanins. A Phytochemicals entry noted that the compound’s color varies depending on the pH level of the solution. According to the article, cyanidin is is red when pH is below 3, blue at pH higher than 11, and violet at neutral pH.
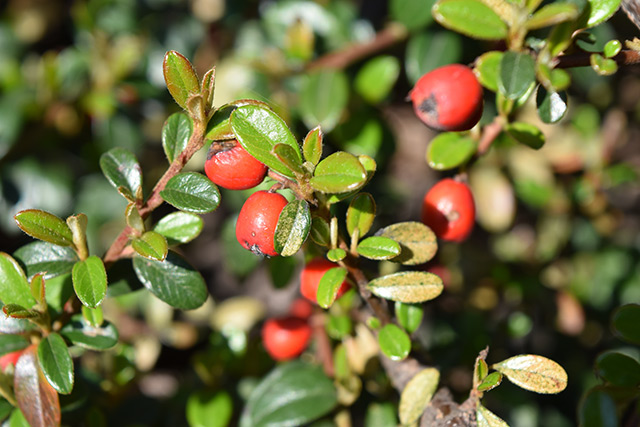
The nutrient can be found in great abundance in berries such as raspberry, bilberry, blackberry, and blueberry as well as cranberry, elderberry, hawthorn, and loganberry. Likewise, other fruits such as apples, peaches, plums, and pears are excellent sources of cyanidin. The fruits’ skins contain the highest cyanidin concentration.

Medicinal uses for cyanidin
Cyanidin is a highly effective anthocyanin that combats the proliferation of cancer. The compound contains strong antioxidant and anti-mutagenic properties that ward off harmful free radicals and neutralize various reactive oxygen types such as hydrogen peroxide, reactive oxygen and hydroxyl radical.
A vast number of in-vivo and in-vitro studies have also demonstrated that the nutrient induces cancer cell death, inhibits cancer cell growth, and prevents cellular damage. The compound is touted to ward off leukemia, lung cancer, colon cancer, skin cancer, and prostate cancer.
The compound is also shown to promote heart health by increasing the levels of endothelial nitric oxide synthase and heme oxygenase. The beneficial nutrient is found to mitigate the formation of reactive oxygen as well. This, in turn, reduces the risk of developing various cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, stroke and heart attacks. Likewise, cyanidin is known to prevent the onset of myocardial ischema.
Cyanidin may help reduce the risk of diabetes too. The anthocyanin is touted to improve the body’s insulin sensitivity and blood glucose rates, according to an entry on the EZine Articles website. A Japanese study notes that the nutrient significantly reduces the expression of retinol-binding protein 4, which in turn results in better glucose control and weight management. Cyanidin is also touted to reduce the risk of fatty liver disease.
In addition, cyanidin is found to improve memory and overall brain health. A Kyle Norton blog entry shows that the compound contains potent neuroprotective properties that help mitigate neuronal death. The nutrient is also found to improve short-term spatial recognition and memory.
Cyanidin also contains anti-inflammatory properties that help stave off a host of inflammation-related diseases. The nutrient is touted to reduce the serum level of malonaldehyde, which serves as a biomarker for oxidative stress. The compound is shown to alleviates arthritis and other inflammatory disorders.
Moreover, cyanidin plays an essential role in the regeneration of rhodopsin, a compound that helps the retina absorb light. This improves the eye’s ability to see at night. The nutrient is also known to keep age-related macular degeneration in check.
People trying to lose weight may benefit from eating foods rich in cyanidin as the compound is shown to increase muscle gain while simultaneously mitigating fat gain. Likewise, cyanidin is touted to prevent the onset of cell aging and significant tissue loss.
Furthermore, cyanidin is found in fortify the body’s overall immunity. The nutrient possesses strong antimicrobial properties that ward off a plethora of infections. In fact, a study notes that the compound helps inhibit the biofilm formation and adhesion to the artificial surface of various bacteria such as Candida parapsilosis, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Escherichia coli, Enterococcus faecalis and Streptococcus mutans.
Body systems supported by cyanidin
Cyanidin is particularly beneficial in inhibiting cancers that attack the lungs, skin, prostate, colon and the circulatory system. Likewise, the compound promotes heart, brain and digestive health. The nutrient also maintains healthy eyes, muscles and immune system.
Where to learn more
- Wealth Opportunity: Blue Honeysuckle Berries are Hottest New Superfood
- Super nutrient sacrifices itself to prevent cellular damage and disease
- Cherries a superfood? Research confirms this well-known fruit tackles cancer, insomnia, high blood pressure and gout
- Sweet potato is a healthy, natural medicine
- Top 8 Foods That Help Digestion
- The health benefits of acai berry
Summary
Cyanidin wards off various types of cancer, heart disease, brain disorders.
Cyanidin prevents arthritis, fatty liver, infections and eye disease.
Cyanidin is beneficial to the heart, brain and the immune system.
Cyanidin also supports the digestive tract, bone and joints and the eyes.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: Cyanidin